Using a routine blood sample, investigators have developed an extremely sensitive assay to detect and quantify DNA fragments containing rare genetic mutations in a patient’s cancer cells. This assay uses “SuperSelective” PCR primers that virtually ignore abundant closely related non-mutant DNA fragments derived from patients’ normal cells. This new assay is faster and considerably cheaper than current methods and can be performed on widely available instruments. The investigators demonstrate the ease of utility of this approach in a new report in the Journal of Molecular Diagnostics.
“The long-term goal of this research is to develop highly multiplex assays that enable both the early detection of mutations relevant to cancer before any symptoms have occurred and the application of an effective early treatment. These assays will use noninvasive liquid biopsies (routine blood samples) taken during a person’s annual medical checkup, and the DNA fragments transiently present in the blood sample (originating from cells that have died) will then be analyzed by highly multiplex real-time or digital PCR techniques,” explained lead investigators Diana Yaneth Vargas, MS, and Fred Russell Kramer, Ph.D., from the Public Health Research Institute of the New Jersey Medical School of Rutgers University, Newark, NJ, U.S.
Current techniques for analyzing liquid biopsies involve either next-generation sequence analysis, which is expensive, lengthy, and has limited sensitivity; or use a PCR technique in which both the mutant DNA fragments and the closely related wild-type DNA fragments are amplified, limiting sensitivity when the mutant DNA fragments are rare. The unique design of SuperSelective PCR primers, on the other hand, enables the amplification of the mutant DNA fragments, while effectively preventing the amplification of the abundant closely related wild-type DNA fragments. Consequently, the SuperSelective PCR assays described in this report are very sensitive.
Multiplex SuperSelective PCR assays, utilizing frequent non-invasive liquid biopsies, enable the choice and subsequent modification of an effective targeted therapy for the treatment of an individual’s cancer. Furthermore, after treatment, these assays may help monitor the patient to detect the presence of minimal residual disease, enabling further intervention if necessary.
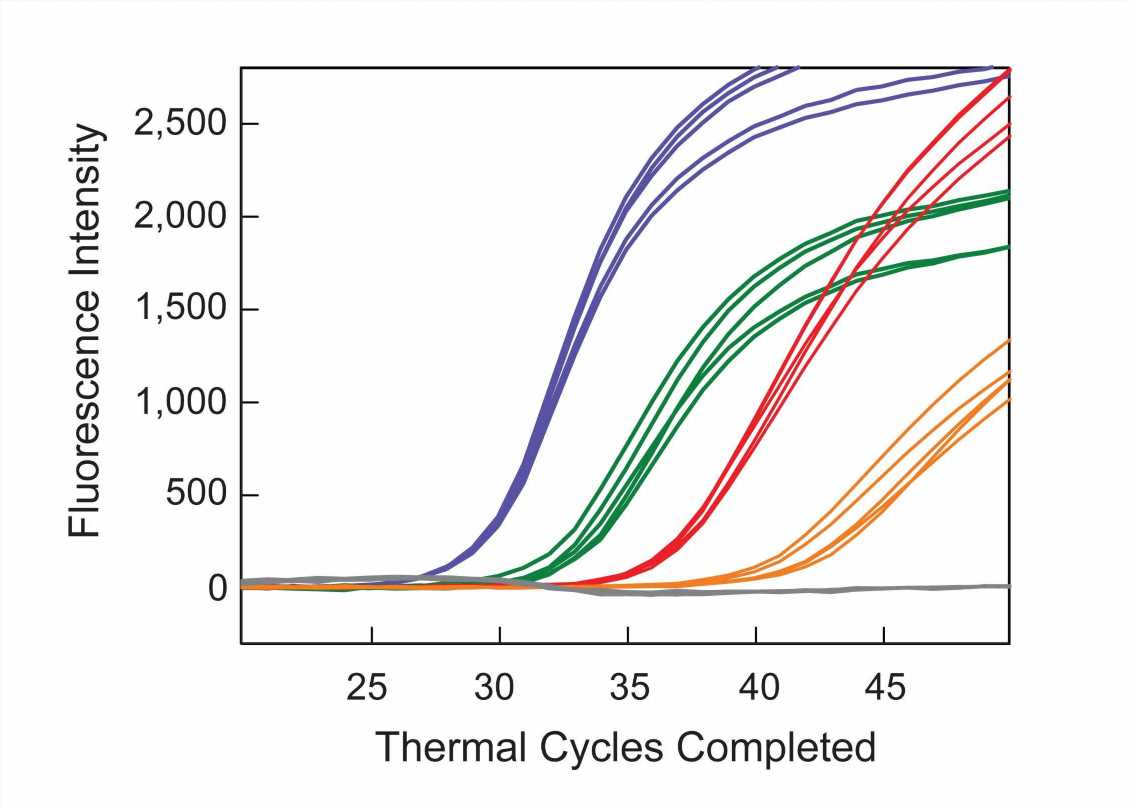
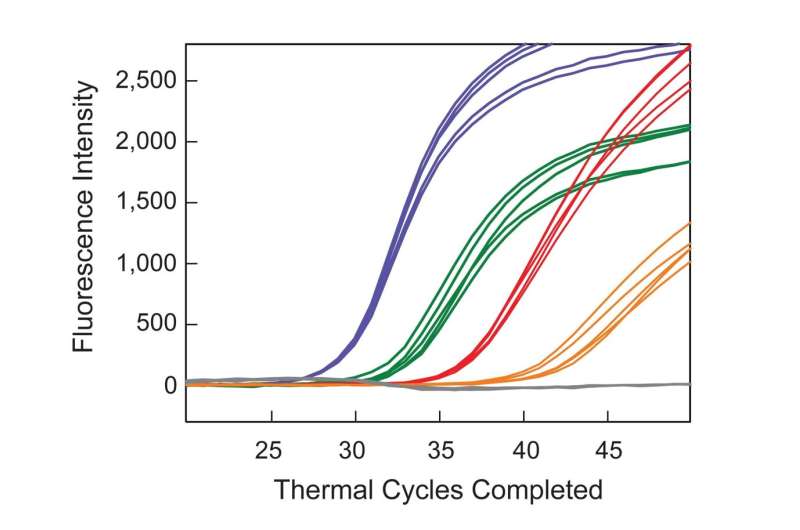
To demonstrate the clinical potential of their approach, six DNA samples from the plasma of patients with cancer were assayed. The samples from five of the patients were blinded. Multiplex SuperSelective PCR assays were performed to confirm the presence or absence of particular human epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutations in each sample. These mutations were chosen because their presence determines which targeted therapy is most likely to be effective against non-small-cell lung cancer. Four samples were positive for different EGFR target mutations and two samples did not give signals for EGFR target mutations. After the blinded samples were unblinded, it was revealed that the two negative samples were from patients who did not have EGFR mutations, and those samples were purposely provided as a control. The assays identified the previously known mutations in the other samples. Significantly, the assay also identified a very rare resistance mutation in one blinded sample that was not previously known to be present, suggesting that the patient’s targeted therapy needed to be changed.
“The only difference between these assays and conventional multiplex real-time PCR is the substitution of SuperSelective primers for conventional primers,” the investigators said. “These assays can be performed rapidly at points of care, and the results can immediately be used to inform subsequent clinical decisions.”
Source: Read Full Article