Blood oxygen level is the amount of oxygen circulating in the blood. Red blood cells carry most of the oxygen, collecting it from the lungs and delivering it to all parts of the body.
The body closely monitors blood oxygen levels to keep them within a specific range so that there is enough oxygen for the needs of every cell.
A person’s blood oxygen level is an indicator of how well the body distributes oxygen from the lungs to the cells, and it can be important for people’s health.
Normal and low blood oxygen levels

A healthy blood oxygen level varies between 75 and 100 millimeters of mercury (mm Hg).
When arterial blood gas (ABG) test results reveal an oxygen level below 60 mm Hg, the medical community considers it low. In some cases, people with these results may require oxygen supplementation.
A blood oxygen level that is too low compared with the average level of a healthy person can be a sign of a condition known as hypoxemia. This develops when the body has difficulty delivering oxygen to all of its cells, tissues, and organs.
Oxygen saturation
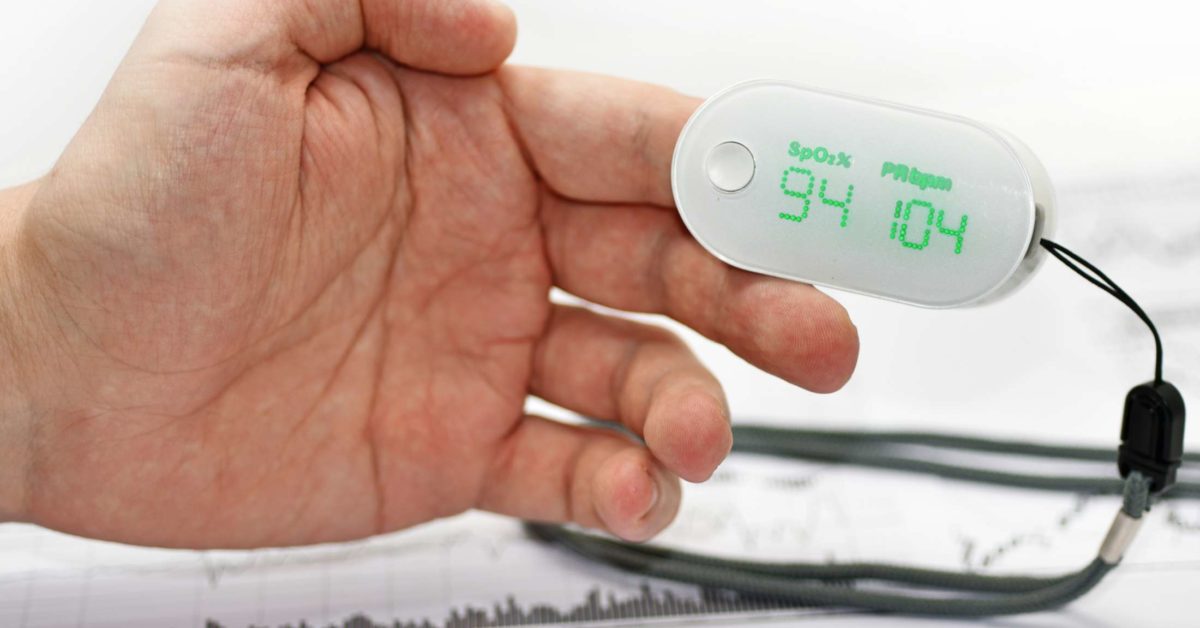
Oxygen saturation refers to the percentage of oxygen in a person’s blood. Medical professionals often use a device called a pulse oximeter for either a quick test or continuous monitoring. The device can attach to the person’s fingertip.
A healthy oxygen saturation level ranges between 95% and 100%. If a person’s levels drop below this range, they may experience symptoms associated with a lack of oxygen, such as trouble breathing and confusion.
How is blood oxygen level measured?
An ABG test is the most effective way to monitor blood oxygen levels. This test involves taking a blood sample from an artery, usually in the wrist. This procedure is very accurate, but it can be a little painful.
Doctors carry out ABG tests in a hospital. However, people can also test themselves at home using a small device known as a pulse oximeter.
A pulse oximeter is a small clip that often attaches to a finger, although it will also work on an ear or a toe. It measures blood oxygen indirectly by light absorption through a person’s pulse.
Although the pulse oximeter test is easier, quicker, and less painful than the ABG test, it is not as accurate. Several factors can interfere with the results, including:
- dirty fingers
- bright lights
- darker skin tones
- nail polish
- poor circulation to the extremities
Learn how to choose the best pulse oximeter to purchase.
Symptoms of low blood oxygen levels
Low blood oxygen levels can result in abnormal circulation and cause the following symptoms:
- shortness of breath
- headaches
- restlessness
- dizziness
- rapid breathing
- chest pain
- confusion
- high blood pressure
- lack of coordination
- visual disorders
- sense of euphoria
- rapid heartbeat
Learn more about the symptoms of poor circulation.
Causes of low blood oxygen
The medical term for low blood oxygen is hypoxemia. It may happen due to:
- insufficient oxygen in the air
- inability of the lungs to inhale and send oxygen to all cells and tissues
- inability of the bloodstream to circulate to the lungs, collect oxygen, and transport it around the body
Conditions that can lead to hypoxemia
Several medical conditions and situations can contribute to the above factors, including:
- asthma
- heart diseases, including congenital heart disease
- high altitude
- anemia
- COVID-19
- chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
- interstitial lung disease
- emphysema
- acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS)
- pneumonia
- obstruction of an artery in the lung
- pulmonary fibrosis, or scarring and damage to the lungs
- presence of air or gas in the chest that makes the lungs collapse
- excess fluid in the lungs
- sleep apnea, which involves breathing interruptions during sleep
- certain medications, including some narcotics and pain relievers
When to contact a doctor
People should contact a doctor if they:
- experience severe and sudden shortness of breath
- experience shortness of breath when at rest
- have severe shortness of breath that worsens during exercise or physical activity
- wake suddenly with shortness of breath or a feeling of choking
- are at high altitude and experience severe shortness of breath with a cough, rapid heartbeat, and fluid retention
Treatment
The treatment options for low blood oxygen levels include supplemental oxygen. Doctors can administer oxygen therapy in an office, or they can prescribe or recommend the use of home oxygen therapy (HOT).
A range of devices is available for delivering and monitoring HOT, but some require a prescription.
People can make lifestyle adjustments to reduce the symptoms of low oxygen levels, as well as improve their general health and quality of life. Changes that will likely be beneficial include:
- quitting smoking
- avoiding secondhand smoke
- eating a nutritious diet containing plenty of fruits, whole grains, lean protein, and vegetables
- exercising regularly
Learn more about following a well-balanced diet.
Outlook
Many conditions can cause low blood oxygen levels. Treating the underlying condition responsible will generally improve blood oxygen levels.
People living with chronic lung diseases, such as COPD, and those who catch COVID-19 may need regular blood oxygen monitoring.
A person with low blood oxygen can also make lifestyle changes, such as adjusting their dietary and exercise habits. In conjunction with oxygen therapy, these changes could help a person raise their oxygen saturation levels.
Summary
A person’s blood oxygen level refers to the amount of oxygen circulating in their blood. A person can measure their blood oxygen levels using a pulse oximeter. On a pulse oximeter, doctors consider levels under 95% to be low.
Several conditions can cause low blood oxygen levels, including asthma, anemia, and COVID-19.
The treatment will often involve addressing the underlying cause, but doctors may sometimes also recommend oxygen therapy or lifestyle modifications.
Read the article in Spanish.
Last medically reviewed on November 29, 2021
Source: Read Full Article